Networking
We offer an extensive range of brands for all types of networking equipment to best suite your office environment requirements and needs.
In today's connected world, reliable networking equipment is the backbone of any organization. Whether you're setting up a small office network or a large enterprise infrastructure, choosing the right equipment can be overwhelming. This content aims to provide an in-depth look at the various types of networking equipment, their functions, and how to select the best options for your needs.
Networking
We offer an extensive range of brands for all types of networking equipment to best suite your office environment requirements and needs.
In today's connected world, reliable networking equipment is the backbone of any organization. Whether you're setting up a small office network or a large enterprise infrastructure, choosing the right equipment can be overwhelming. This content aims to provide an in-depth look at the various types of networking equipment, their functions, and how to select the best options for your needs.
Types of Networking Equipment

Routers
These devices connect multiple networks together and route traffic between them. They're essential for internet connectivity and come in various forms, including wired, wireless, and virtual routers.

Switches
Switches connect devices within a network, allowing them to communicate with each other. They're available in different sizes, speeds, and configurations, including managed, unmanaged, and PoE (Power over Ethernet) switches.

Firewalls
Firewalls are network security systems that monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. They can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both.

Access point
Access points (APs) provide wireless connectivity to devices, allowing them to connect to a network. They're commonly used in Wi-Fi networks and come in various forms, including indoor, outdoor, and mesh APs.

Network Interface Cards (NICs)
NICs are hardware components that connect devices to a network. They're available in various forms, including Ethernet cards, Wi-Fi adapters, and fiber optic cards.

Modems
Modems connect devices to the internet via a broadband connection. They're available in various forms, including DSL, cable, and fiber optic modems.

Network Attached Storage
NAS devices provide centralized storage for files and data, allowing multiple devices to access and share files.

Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Injectors
PoE injectors provide power to devices over Ethernet cables, eliminating the need for separate power sources.
Network Storage
Network Storage also known as network-attached storage (NAS), is a type of storage device that connects to a network, allowing multiple devices to access and share files. Here are some key aspects of network storage.
Types of Network Storage

Network Attached Storage (NAS)
A dedicated device that provides file-level storage and sharing capabilities.
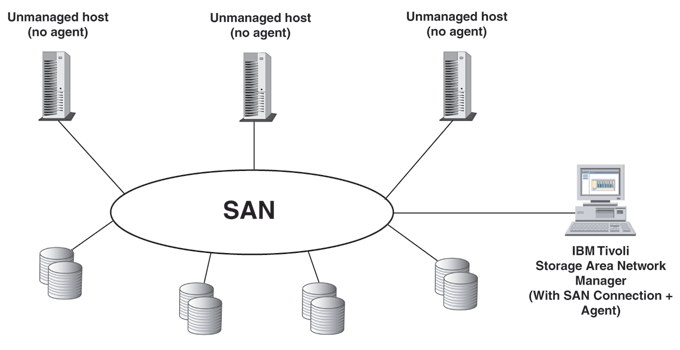
Storage Area Network
A high-speed network that provides block-level storage and is typically used for large-scale enterprise storage.

Cloud Storage
Network storage can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing storage needs.
Benefits of Network Storage
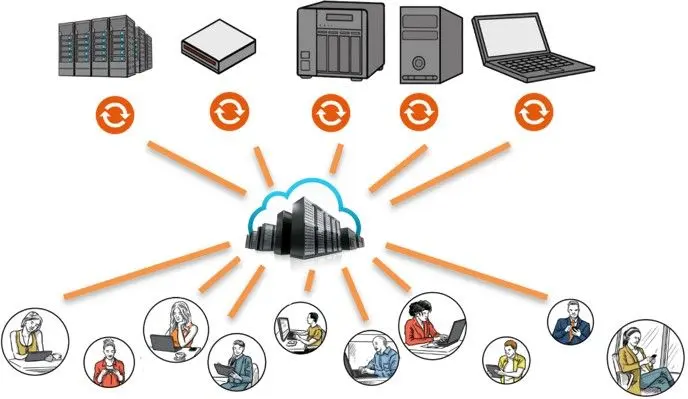
Centralized Storage
Network storage provides a centralized location for storing and managing files, making it easier to access and share data.

File Sharing
Network storage allows multiple devices to access and share files, making it ideal for collaborative work environments.

Data Protection
Network storage often includes features such as redundancy, backup, and disaster recovery, which help protect data from loss or corruption.

Cloud Scalability
Network storage can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing storage needs.
Servers
The unsung heroes of the digital world. Let's dive into the fascinating realm of servers.
Servers are powerful computers or software programs designed to manage, process, and provide access to resources, data, or services over a network. They can be thought of as the central hub of a network, handling requests, and delivering information to clients (like your laptop or smartphone).
Types of Servers

Web Servers
Host websites, web applications, and serve content over the internet (e.g., Apache, Nginx).

Database Servers
Store and manage data, providing access to databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL).

File Servers
Store and manage files, allowing users to access and share them (e.g., FTP, SFTP).
Mail Servers
Manage email services, storing and forwarding emails (e.g., SMTP, IMAP).

Game Servers
Host online gaming sessions, managing game state and player interactions.

Cloud Servers
Virtual servers running in cloud environments (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).

Application Servers
Host and manage applications, providing a platform for development and deployment.
Servers Technologies and Trends

Virtualization
Creating virtual servers to improve resource utilization and scalability.

Containerization
Using containers (e.g., Docker) to deploy and manage applications.

Cloud Computing
Leveraging cloud services for scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.

Server-less Computing
Running applications without managing servers (e.g., AWS Lambda).
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Integrating AI and machine learning into server infrastructure.
Challenges and Considerations

Security
Protecting servers from cyber threats and data breaches.

Scalability
Ensuring servers can handle increased traffic and demand.
Performance
Optimizing server performance for fast response times.

Maintenance
Regularly updating and maintaining server software and hardware.
Tailor-Made Rental Options available
Terms and Conditions Apply